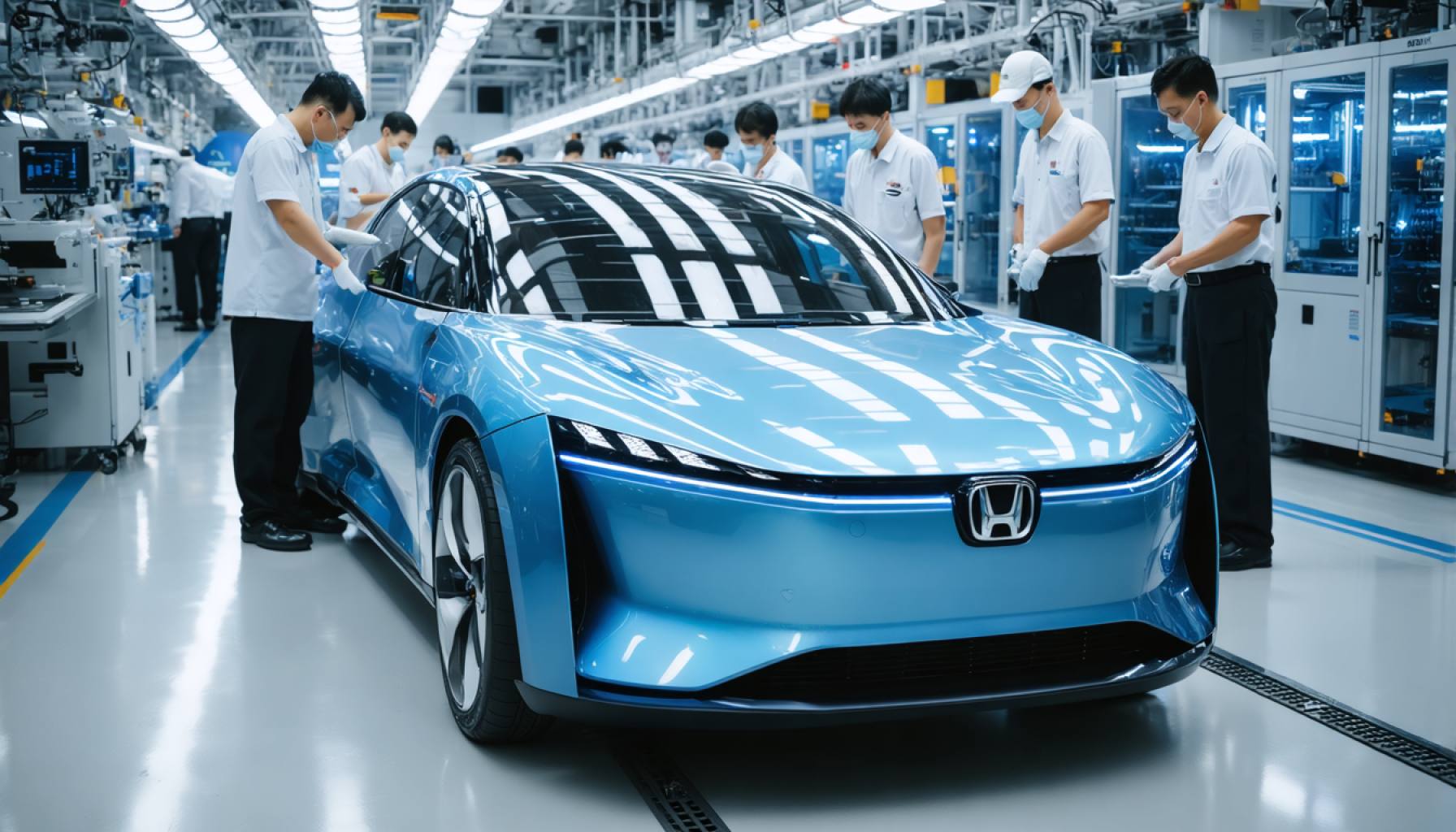
- Honda’s new EV plant highlights a significant reduction in human labor by 30% through advanced automation.
- The facility utilizes AI and robotics for tasks like welding, assembly, painting, and quality inspection, ensuring high efficiency and accuracy.
- Data-driven systems optimize production, minimize errors, and anticipate maintenance needs to reduce downtime.
- This move aligns Honda with the broader industry trend towards sustainable and efficient automotive manufacturing.
- The plant represents a shift towards less carbon-intensive manufacturing, with implications for the workforce and potential upskilling opportunities.
- Honda’s strategic advancements underscore the symbiotic relationship between innovation and sustainability in the EV market.
Nestled in the pulsating heart of China’s automotive industry, Honda’s new electric vehicle (EV) plant emerges as a glittering testament to the future of manufacturing. Here, metallic arms whirr and pivot with the precision of a well-choreographed ballet, bringing vehicles to life with an efficiency that boasts a staggering 30% reduction in human labor. This isn’t just another factory; it’s a marvel of modern engineering and technology, a place where artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics collaborate seamlessly to set new industry benchmarks.
Shifting gears from traditional methods, Honda has designed this cutting-edge facility to harness the full potential of automation. Instead of rows of workers, the factory floor is dominated by sleek robotic systems capable of intricate tasks, from welding and assembling to painting and quality inspection. These machines don’t tire, don’t waver, and execute their programmed tasks with unwavering accuracy.
By leaning heavily on AI and robots, Honda is reducing costs, minimizing errors, and accelerating production times. The data-driven machines evaluate each component’s integrity, adjusting processes on the fly to maintain the highest quality standards. This data is constantly fed back into a central system that optimizes workflow and anticipates maintenance needs, ensuring minimal downtime.
But beyond the mechanical awe, there’s a deeper narrative at play. This shift not only reflects Honda’s strategic move to remain competitive in the EV market but also underscores a broader trend within the automotive industry—a commitment to sustainable and efficient production practices. As global demand for electric vehicles surges, driven by environmental imperatives and consumer preferences, manufacturers like Honda are betting big on technology to meet these needs.
The implications of Honda’s technological leap extend far beyond the assembly line. It signifies a move toward a less carbon-intensive manufacturing process—one that’s crucial for reducing the environmental footprint of car production. The reduced dependence on human labor also sparks discussions on workforce evolution, urging stakeholders to consider how they can upskill and transition existing employees for future roles in such tech-forward environments.
Indeed, Honda’s plant is more than just a factory; it’s a bold statement about the future of automotive production. The message is clear: Innovation and sustainability are not at odds but are motors driving us toward a cleaner, more efficient, and more intelligent industrial landscape.
Unveiling Honda’s Revolutionary EV Plant: Insights, Strategies, and Future Implications
The unveiling of Honda’s new electric vehicle (EV) plant in China not only marks a significant technological achievement but also serves as a catalyst for change in the global automotive landscape. As the facility brims with cutting-edge robotics and artificial intelligence, it embodies a shift towards a more sustainable, efficient, and innovative manufacturing future. Here’s a deeper dive into the facet of Honda’s venture that weren’t fully explored in the source material.
How-To Steps & Life Hacks
1. Transitioning to Automated Production: Companies looking to emulate Honda’s success should start by auditing their current operations to identify areas ripe for automation. Begin with processes that are repetitive and have a high margin for error.
2. Implementing AI in Quality Control: Integrate AI systems that can predict defects and inefficiencies in real-time. This could involve adopting machine learning algorithms capable of processing vast data sets quickly.
3. Upskilling the Workforce: Develop training programs focusing on robotics, AI, and data analytics to help current employees transition into more tech-oriented roles.
Real-World Use Cases
– Reduced Error Rates: Honda’s AI systems lead to markedly lower error rates in vehicle assembly, enhancing product reliability and consumer trust.
– Environmental Benefits: The decrease in manual labor and energy-efficient robots result in a reduced carbon footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals.
Market Forecasts & Industry Trends
– Growing EV Demand: As governments worldwide push for lower emissions and consumers gravitate towards sustainable options, the demand for EVs is expected to surge. BloombergNEF predicts that by 2040, EVs will make up 58% of global passenger car sales.
– Automation Adoption: A shift towards greater automation, akin to Honda’s strategy, is forecasted across numerous sectors, with the automotive industry at the forefront.
Reviews & Comparisons
– Comparative Advantages: Honda’s plant outperforms traditional factories with its 30% reduction in human labor, indicating potential cost savings and increased production speeds.
– Technological Prowess: The integration of real-time monitoring systems places it ahead of competitors in maintaining quality consistency.
Controversies & Limitations
– Workforce Displacement: One challenge of shifting to automated systems is the potential workforce displacement, necessitating significant reskilling initiatives.
– Initial Investment Costs: The upfront cost for state-of-the-art automation can be high, posing a barrier for smaller manufacturers.
Features, Specs & Pricing
– Robotics and AI Integration: A suite of robotic arms capable of welding, painting, and assembling, paired with AI-driven analytics systems.
– Cost Efficiency: While specific pricing of the technology may vary, reduced labor costs and increased throughput can offset initial investment over time.
Security & Sustainability
– Minimized Downtime: Predictive maintenance enabled by AI ensures the plant operates efficiently with minimal disruption.
– Sustainable Practices: The plant represents a leap forward in reducing industrial carbon emissions, setting a benchmark for sustainability in manufacturing.
Insights & Predictions
– Evolving Industry Dynamics: As automation becomes commonplace, companies must adapt their business models, prioritizing flexibility and innovation.
– Future Workforce: Expect the emergence of specialized roles around AI system management and maintenance.
Tutorials & Compatibility
– Integrating New Technologies: Tutorials on adopting automated solutions should focus on system integration without disrupting existing workflows.
– Sensor and Data Compatibility: Ensure that all new technologies deployed are compatible with enterprise-wide data architectures.
Pros & Cons Overview
Pros
– Increased production speed
– Lower operational costs
– Enhanced product quality
Cons
– High upfront costs
– Potential skill gaps
– Ethical considerations around employment
Actionable Recommendations
– Invest in Training: Companies should allocate resources to reskill their workforce in AI and robotics to bridge any skill gaps.
– Adopt a Phased Approach: Gradually implement automation technologies to manage costs and workforce impact effectively.
– Evaluate Environmental Impact: Regular assessments of energy consumption and emissions can further enhance sustainability efforts.
Honda’s innovative plant sets a new precedent for the automotive industry, emphasizing the seamless integration of technology and sustainability. By adopting similar strategies, manufacturers can improve operational efficiency and embrace a future-oriented business approach.
For more insights on innovation in the automotive sector, visit Honda.